
- #Tcp checksum update
- #Tcp checksum driver
- #Tcp checksum full
- #Tcp checksum software
- #Tcp checksum free
Network adapters commonly support LSO or TSO. The host system simply shuttles outgoing data from memory to the network controller's buffer and the network controller segments the outgoing data into packets and facilitates their transmission. LSO/TSO offloads the networking tasks of all outgoing data. Since checksum calculations and checks take time, offloading those tasks from the CPU will boost performance without a wholesale re-architecting of the operating system's TCP/IP stack.Īnother popular alternative is the large segment offload (LSO) technique, or TSO. One alternative is TCP checksum offload the system CPU still shuttles data and assembles/disassembles header information but the network controller calculates checksum, inserts it into the packet and validates it during reception.
#Tcp checksum full
Given the criticisms of full TCP offload products, some IT professionals choose another route.
Always refer to vendor documentation for enabling or disabling offload features. When the offload engine is software-based, such as Microsoft's TCP Chimney, you may need to access the system registry and disable the appropriate registry key. Alternatively, try to disable offload features in the Advanced tab of the connection's Properties dialog under Windows. If the offload adapter is in a PCIe slot, try accessing the BIOS through a dedicated utility provided with the adapter. If the network controller is integrated onto the system's motherboard, you can access the system BIOS during a reboot cycle. If you must disable the network controller's offload capability for testing or troubleshooting, check for enable/disable controls in the network controller's BIOS. As with any upgrade, test changes in a lab setting first.
#Tcp checksum driver
Similarly, look for driver updates for the host and virtual machines' operating systems. If the offload engine is deployed as a PCI Express (PCIe) adapter, evaluate firmware upgrades for the adapter rather than the motherboard.
#Tcp checksum update
For example, if the offload engine is integrated onto the system's motherboard, consider a motherboard firmware update to address networking problems.
#Tcp checksum software
When troubleshooting offload engine issues, always consider software updates or upgrades, usually firmware or driver updates. If a server completes tasks faster than the TCP offload controller can acknowledge a transmission, it can cause communication errors.Īlmost all functional or performance problems with TCP/IP offload products relate to software.

Host systems are constantly getting faster next-generation hosts without offload controllers handle networking better than older systems with offload controllers. Not every data center will reap benefits from TCP offload. Proprietary TCP offload implementations can require extensive changes to the TCP/IP stack, degrading support and security, adding complexity and hurting Quality of Service, along with other network features. Network performance problems occur if the controller is overtaxed. TCP offload controllers are more likely than other controllers to suffer resource shortages. In spite of the promise of TCP offload technologies, adoption is limited. TCP offload is no cure-all for network ailments Although features and functionality may vary based on the actual offload product, all three classifications serve essentially the same purpose. TCP Chimney Offload is Microsoft's software offload feature. TCP segmentation offload (TSO) is used in some virtual environments, such as VMware. TCP/IP offload engine (TOE) is the term coined by hardware-based network controller vendors. TCP Chimney, TSO and TOE all refer to offload technology. The controller handles all of the packet formation, checksum, buffering and other tasks, and exchanges blocks of data with the host.
#Tcp checksum free
To free the CPU from overhead networking tasks, the network controller took over processing the entire TCP/IP stack on dedicated hardware. Some modern data center technologies, such as iSCSI and other network-based storage and virtualization, impose networking demands on the processor.
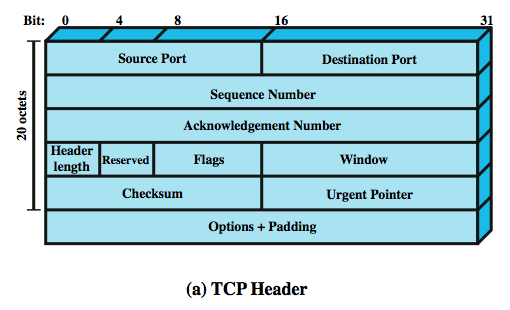
This processing overhead increases when data centers adopt high-bandwidth 1 Gigabit Ethernet or 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks. Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) network communication imposes overhead on the processor, which handles workload computing tasks. CPUs also handle network data reception - essentially the reverse of transmission tasks. In traditional networking, the CPU handles every major task involved with transmitting data: direct memory access to stage outgoing packet data, calculating the checksum for each packet, adding header information and moving packets to the network interface buffer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
